Temperature is one of the most familiar yet scientifically significant measurements in everyday life. It influences how we dress, how our bodies feel, how machines operate, how food is cooked, and how nature behaves. Among the many temperature-related questions people ask, converting 30 degrees C to F is one of the most common. This is because Celsius and Fahrenheit are the two most widely used temperature scales in the world, and understanding the relationship between them helps bridge communication across regions, professions, and daily activities.
This article provides a comprehensive, original, and detailed explanation of 30 degrees Celsius converted to Fahrenheit. It goes far beyond a simple numerical answer and explores the science behind temperature scales, the historical background, practical uses, real-world implications, conversion methods, common misconceptions, and why this specific temperature value is so relevant in everyday life. The goal is to deliver a deep, informative resource written entirely in original language, with clear explanations, structured sections, and helpful tables where appropriate.
Understanding Temperature and Measurement Scales
Temperature is a physical quantity that measures the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance. In simpler terms, it tells us how hot or cold something is. When particles move faster, the temperature is higher; when they move slower, the temperature is lower. Humans experience temperature subjectively as warmth or cold, but science requires standardized scales to measure it accurately.
Different temperature scales exist because they were developed in different historical and scientific contexts. The most commonly used scales today are Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin. Celsius is widely used in most countries for weather, science, and daily life. Fahrenheit is mainly used in the United States and a few other regions, especially for weather and household temperature references. Kelvin is primarily used in scientific research.
Understanding how 30 degrees Celsius relates to Fahrenheit requires understanding how these scales differ in structure, reference points, and increments.
The Celsius Scale Explained
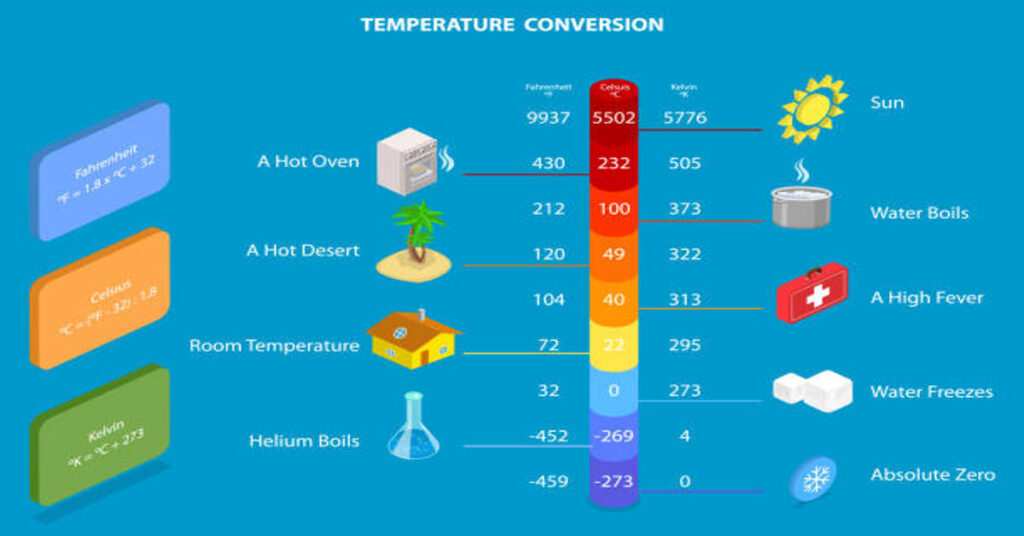
The Celsius scale is based on the properties of water, which makes it intuitive and practical for everyday use. On the Celsius scale, water freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees under standard atmospheric pressure. This creates a simple and logical range that aligns well with common environmental temperatures.
Celsius is widely used in weather forecasts, cooking, healthcare, and education across most of the world. When someone says it is 30 degrees Celsius outside, people familiar with this scale immediately understand that the weather is quite warm, often associated with summer conditions.
The simplicity of the Celsius scale makes it easier to interpret temperature changes. A difference of 10 degrees represents a meaningful and noticeable change in environmental conditions.
The Fahrenheit Scale Explained
The Fahrenheit scale was developed earlier than Celsius and uses different reference points. On this scale, water freezes at 32 degrees and boils at 212 degrees under standard atmospheric pressure. This creates a range of 180 degrees between freezing and boiling, compared to 100 degrees in Celsius.
Fahrenheit is commonly used for weather reporting in the United States. One reason people appreciate Fahrenheit for weather is that it provides smaller increments, which can make temperature changes feel more precise. For example, a difference of 5 degrees Fahrenheit represents a relatively small but noticeable change in comfort.
When converting 30 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, understanding these reference points helps explain why the resulting number seems much higher than 30.
The Exact Conversion of 30 Degrees C to F
To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, a specific mathematical relationship is used. The formula reflects the different zero points and interval sizes of the two scales.
The conversion formula is:
Fahrenheit = (Celsius × 9/5) + 32
Applying this formula to 30 degrees Celsius gives:
30 × 9/5 = 54
54 + 32 = 86
So, 30 degrees Celsius is equal to 86 degrees Fahrenheit.
This result explains why 30°C feels like a hot day in regions that use Fahrenheit. An 86°F day is typically associated with summer heat, outdoor activities, and the need for hydration and sun protection.
Conversion Table for Context
To better understand where 30°C fits within a broader range, the table below provides nearby Celsius values and their Fahrenheit equivalents.
| Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 20°C | 68°F | Mild and comfortable |
| 25°C | 77°F | Warm and pleasant |
| 30°C | 86°F | Hot summer weather |
| 35°C | 95°F | Very hot conditions |
| 40°C | 104°F | Extreme heat |
This table shows that 30 degrees Celsius sits firmly in the hot weather category, especially for people not accustomed to high temperatures.
What 30 Degrees Celsius Feels Like
Understanding the numerical conversion is important, but understanding how 30°C feels is equally valuable. At this temperature, the human body begins to experience noticeable heat stress, especially if humidity is high or if physical activity is involved.
In dry conditions, 30°C can feel warm but manageable, particularly with shade and airflow. In humid conditions, however, the same temperature can feel significantly hotter because sweat evaporates more slowly, reducing the body’s ability to cool itself. This is why weather reports often include a “feels like” temperature, which accounts for humidity.
For many people, 30°C is the point where light clothing, sunscreen, and increased water intake become essential for comfort and health.
Importance of 30°C in Weather and Climate
In meteorology, 30 degrees Celsius is often used as a benchmark for hot weather. Many weather services consider temperatures at or above this level as heat conditions that may impact daily life, agriculture, and energy consumption.
In some regions, 30°C is common during summer months, while in others it may be considered extreme. Climate patterns, latitude, altitude, and proximity to oceans all influence how frequently this temperature occurs.
From a climate perspective, the increasing frequency of days reaching or exceeding 30°C in some regions is often discussed in relation to global warming and urban heat effects. This makes understanding the conversion to Fahrenheit especially important for global climate communication.
Role of 30 Degrees Celsius in Health and Safety
Temperature has a direct impact on human health, and 30°C is a critical threshold for many health guidelines. At this temperature, prolonged exposure without proper hydration or cooling can lead to heat exhaustion, especially for children, older adults, and people with certain medical conditions.
Health professionals often advise limiting strenuous outdoor activities when temperatures reach around 30°C or higher. Employers in outdoor industries may adjust work schedules to avoid peak heat hours. Understanding that 30°C equals 86°F helps ensure that safety guidelines are correctly interpreted across regions using different temperature scales.
30°C in Daily Life and Practical Applications
Beyond weather, 30 degrees Celsius appears in many practical contexts. In cooking, some fermentation processes and food storage guidelines reference temperatures around this range. In electronics, operating temperatures may be specified in Celsius, making conversion important for technicians in Fahrenheit-based regions.
In travel, understanding temperature conversions helps travelers prepare appropriately for destinations that use a different scale. Knowing that a forecast of 30°C means 86°F allows for better packing decisions and activity planning.
In sports and fitness, training recommendations often adjust intensity when temperatures approach or exceed 30°C to prevent overheating and dehydration.
Why Celsius and Fahrenheit Still Coexist
One might wonder why two different temperature scales are still in use today. The coexistence of Celsius and Fahrenheit is largely due to historical adoption and cultural familiarity. Changing an entire country’s temperature system would require updating infrastructure, education, media, and daily habits.
As a result, conversions like 30 degrees C to F remain highly relevant. They allow people from different regions to communicate effectively about weather, health, science, and daily experiences.
Common Mistakes When Converting 30°C to F
One common mistake is assuming that the conversion is a simple multiplication or addition. Because the scales have different zero points and interval sizes, both multiplication and addition are required. Forgetting to add 32 after multiplying is a frequent error.
Another mistake is confusing Celsius with Kelvin or assuming that 30°C is “just warm” without recognizing its significance in Fahrenheit terms. Understanding the correct conversion helps avoid misinterpretation, especially in safety-related situations.
Mental Shortcuts for Quick Estimation
While the exact formula is best for accuracy, some people use mental shortcuts for rough estimation. One common method is doubling the Celsius value and adding 30. For 30°C, this gives approximately 90°F, which is close to the actual value of 86°F. While not exact, this shortcut can be useful for quick, informal understanding.
However, for professional, scientific, or health-related purposes, the exact conversion should always be used.
Educational Importance of Temperature Conversion
Learning how to convert temperatures like 30°C to Fahrenheit is a fundamental skill in science education. It helps students understand proportional relationships, linear equations, and real-world applications of mathematics.
This knowledge also fosters global awareness by enabling students to interpret international data, weather reports, and scientific studies that use different measurement systems.
Cultural Perception of 30 Degrees Celsius
Cultural background strongly influences how people perceive temperature. In tropical regions, 30°C may be considered normal or even mild, while in cooler climates it may be perceived as intense heat. Converting this value to Fahrenheit helps bridge these cultural perceptions and provides a common reference point.
Understanding these differences promotes better communication, especially in global discussions about climate, travel, and health.
Summary Table: Key Facts About 30°C to F
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Celsius Value | 30°C |
| Fahrenheit Equivalent | 86°F |
| Weather Classification | Hot |
| Common Contexts | Summer weather, travel, health |
| Health Consideration | Risk of heat stress |
This table consolidates the most important information into a clear, easy-to-reference format.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 30 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit?
30 degrees Celsius is equal to 86 degrees Fahrenheit using the standard conversion formula.
Is 30°C considered hot weather?
Yes, 30°C is generally considered hot, especially in humid conditions or for prolonged outdoor activity.
Why does 30°C seem much higher in Fahrenheit?
This is because the Fahrenheit scale uses a different zero point and smaller increments, resulting in higher numerical values.
Can 30°C be dangerous to health?
It can be if proper precautions are not taken, particularly for vulnerable individuals or during physical exertion.
Why is temperature conversion still important today?
Because different regions use different scales, conversions help ensure clear communication in weather, health, science, and travel.