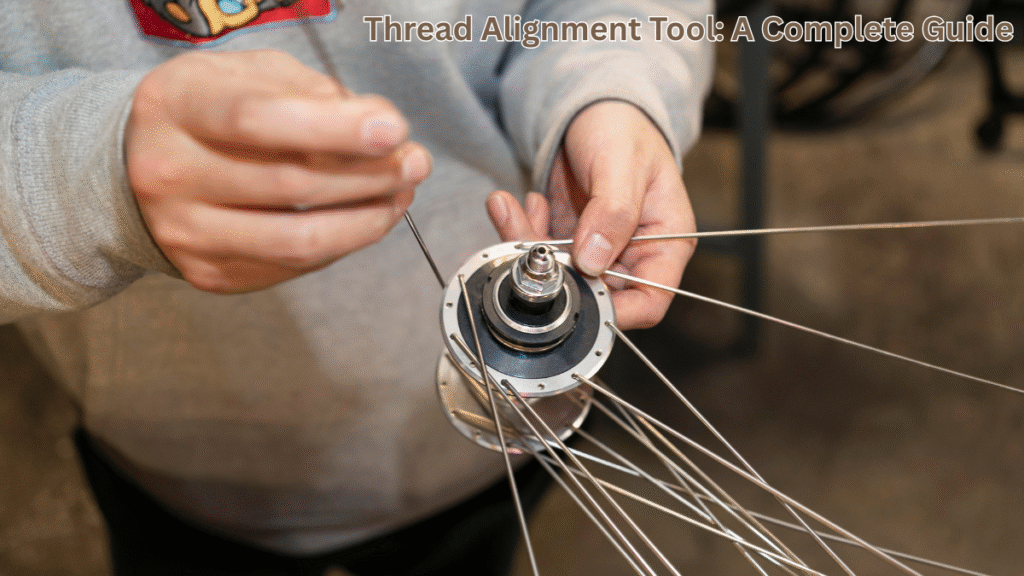
The search for precision in engineering, manufacturing, and even DIY work often leads to one critical challenge: aligning threads correctly. Misaligned threads can strip bolts, damage machinery, or create unsafe conditions. A thread alignment tool is designed to prevent these costly errors by guiding fasteners into proper engagement. Within minutes of use, it saves time, materials, and frustration. This article explores everything you need to know about thread alignment tools—their purpose, working principles, variations, modern advancements, and best practices.
What Is a Thread Alignment Tool?
A thread alignment tool is a specialized device used to ensure that screws, bolts, or other threaded fasteners enter their corresponding threaded holes with perfect alignment. It works by guiding the fastener into the correct path, reducing the risk of cross-threading. Unlike a tap or die that cuts threads, this tool doesn’t alter the structure of threads—it protects them.
The concept might seem simple, but in mechanical work, alignment is as important as strength. When threads are off by even a fraction of a millimeter, they bind, weaken, or fail. The alignment tool solves this by correcting the angle of entry.
Why Thread Alignment Matters
Threaded fasteners are the backbone of machinery, construction, aerospace, and automotive work. But misaligned threads can cause:
- Stripped fasteners that no longer hold
- Equipment downtime from repair or replacement
- Increased costs due to wasted parts
- Reduced safety in load-bearing applications
Imagine an aircraft engine where a misaligned bolt compromises performance, or a car suspension where stripped threads weaken critical joints. The consequences can be catastrophic. Thread alignment tools help avoid such risks, making them essential in industries where safety and accuracy are paramount.
How Does a Thread Alignment Tool Work?
At its core, the tool operates on guiding principles. It aligns the male thread (bolt or screw) with the female thread (nut or hole) before torque is applied. Many designs include adjustable sleeves or self-centering features that stabilize the fastener during insertion.
Steps of use typically include:
- Positioning the tool over the hole or threaded surface.
- Inserting the fastener into the guide sleeve.
- Aligning the fastener to match the axis of the receiving thread.
- Engaging the threads gently until resistance is minimal.
- Securing the fastener with the required torque once aligned.
By minimizing cross-threading, the tool reduces wear on both fastener and component.
Types of Thread Alignment Tools
Thread alignment tools vary based on industry, size, and application. Here are the main categories:
| Type | Description | Common Uses | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Handheld Guides | Simple sleeves or tubes that guide bolts | Automotive repair, DIY | Portable, inexpensive |
| Adjustable Alignment Tools | Tools with adjustable sleeves for different bolt sizes | Maintenance workshops | Versatile, reusable |
| Hydraulic-Assisted Tools | Alignment aided by hydraulic pressure | Heavy machinery assembly | High precision, reduces labor |
| Magnetic Guides | Tools with magnets that hold fasteners in place | Aerospace, electronics | Stable, ideal for delicate work |
| Digital Alignment Systems | Tools with sensors and displays showing alignment | Precision manufacturing | Advanced accuracy, data tracking |
Materials Used in Thread Alignment Tools
Durability is crucial. These tools are commonly made from:
- Hardened steel for heavy-duty applications
- Aluminum alloys for lightweight versions
- Polymer composites in electronics or sensitive industries
- Magnetized steel for stability in vertical alignments
The material choice reflects the environment. For example, aerospace engineers may prefer lightweight composites, while automotive mechanics rely on hardened steel.
Applications Across Industries
Automotive
Mechanics use thread alignment tools during engine rebuilds, suspension work, and transmission assembly. It prevents costly thread damage when reinstalling parts repeatedly.
Aerospace
Every bolt in aircraft must meet strict tolerances. Alignment tools guarantee threads engage correctly without compromising safety.
Manufacturing
On production lines, misalignment slows efficiency. Automated thread alignment tools help maintain speed and consistency.
Construction
In structural steelwork, alignment tools ensure bolts enter beams and plates at correct angles for maximum load-bearing.
Electronics
Miniature fasteners require delicate handling. Precision thread alignment tools prevent damage to fragile casings and circuit housings.
The Evolution of Thread Alignment Tools
Originally, workers relied on experience and careful handwork to avoid cross-threading. Early alignment devices were little more than crude sleeves. Modern engineering has transformed them into sophisticated instruments.
Recent innovations include:
- Laser-guided alignment for ultra-precise applications
- Ergonomic grips to reduce operator fatigue
- Smart sensors that alert users to misalignment
- Hybrid designs combining alignment with torque control
These changes reflect the growing demand for speed and precision in today’s industries.
Benefits of Using a Thread Alignment Tool
- Prevents cross-threading and damage
- Extends the lifespan of fasteners and components
- Improves efficiency during assembly and repairs
- Reduces costs by avoiding replacements
- Enhances safety in load-bearing applications
- Supports sustainability by minimizing material waste
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, the tool has challenges:
- Not always available for extremely small fasteners
- Some designs are expensive for casual users
- Requires training in advanced models
- Over-reliance may reduce technician skill in manual alignment
Manufacturers are addressing these with modular, cost-effective solutions suitable for both experts and beginners.
Best Practices for Using a Thread Alignment Tool
- Always start with clean threads to avoid contamination.
- Use light lubrication when recommended.
- Align gently—never force engagement.
- Verify alignment with a visual inspection before applying torque.
- Store tools properly to prevent wear or distortion.
Thread Alignment vs. Re-Threading
Some confuse alignment with re-threading. Re-threading tools repair damaged threads by cutting or reshaping them. Alignment tools prevent such damage in the first place. Using both ensures threads remain both accurate and durable.
Safety Considerations
Thread alignment tools not only save money but also lives. In heavy industries, improper alignment can cause bolt failures under stress, leading to accidents. Safety protocols recommend always verifying alignment before applying torque.
Cost and Accessibility
Prices vary:
- Basic guides: $20–$50
- Adjustable tools: $80–$150
- Hydraulic or digital systems: $500+
While high-end versions are costly, they pay off in critical applications by avoiding catastrophic failures.
Future of Thread Alignment Tools
Advancements in artificial intelligence and robotics are reshaping the field. We can expect:
- AI-driven self-aligning systems in automated factories
- Augmented reality guidance for technicians
- Eco-friendly materials to reduce environmental impact
- Global standardization for universal usability
The future tool will be smarter, lighter, and more connected.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of a thread alignment tool?
It ensures bolts or screws engage properly with threaded holes, preventing cross-threading and damage.
2. Can I use a thread alignment tool for all fastener sizes?
Some tools are size-specific, but adjustable models cover a wide range of thread diameters.
3. How is a thread alignment tool different from a tap or die?
A tap or die cuts or repairs threads, while an alignment tool guides fasteners without altering them.
4. Are thread alignment tools necessary for home DIY projects?
For critical or expensive parts, yes. Even in small DIY projects, they save time and protect materials.
5. What industries rely most heavily on thread alignment tools?
Automotive, aerospace, construction, electronics, and precision manufacturing are the biggest users.
Conclusion
A thread alignment tool may look modest, but its value lies in preventing problems before they occur. By ensuring that threads engage correctly, it safeguards machinery, saves costs, and enhances safety. From a simple handheld sleeve to a digital AI-driven system, this tool embodies the evolution of engineering precision. Whether you are a DIY enthusiast tightening a bolt at home or an aerospace engineer assembling critical components, the thread alignment tool is an indispensable ally.