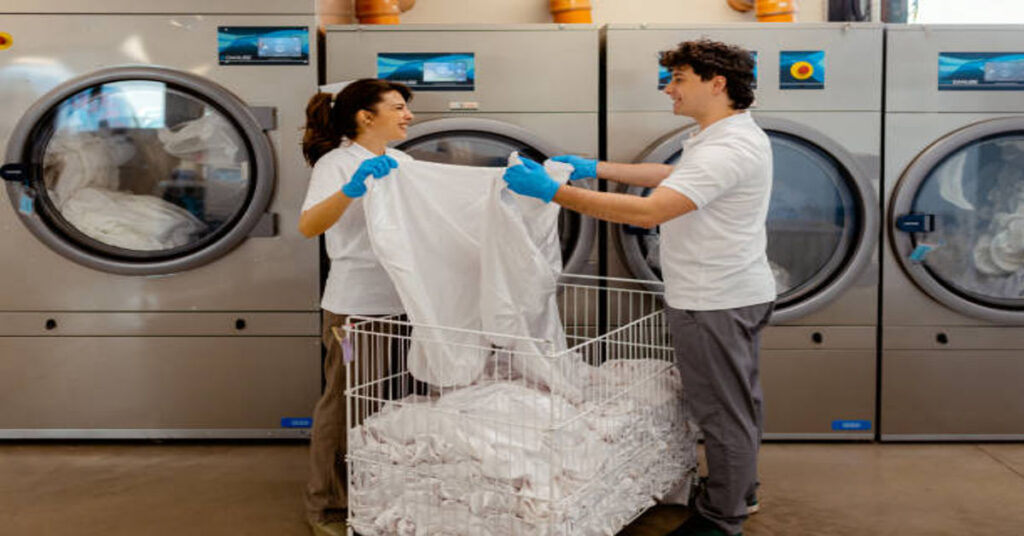
The word “lavanderia” is widely used in Spanish, Italian, and Portuguese-speaking communities, referring to a laundry facility where clothes, linens, and other fabrics are washed, dried, ironed, and cared for. While the term seems simple, the concept of a lavanderia has evolved significantly across decades, transforming from small neighborhood washhouses into technologically advanced cleaning centers serving households, industries, and commercial establishments. This article explores lavanderias in detail, including their history, operations, equipment, environmental influence, modern business models, customer expectations, staff roles, fabric handling techniques, financial considerations for entrepreneurs, and the emerging future of laundry care.
The History and Cultural Evolution of Lavanderia
In earlier centuries, laundry was performed manually in rivers, wells, or communal stone wash basins. These shared wash locations acted not only as utilitarian spaces but also community gathering points. Women exchanged family news, recipes, and social stories as they scrubbed clothes against stone slabs using lye, soap, ash, and natural disinfectants. With the evolution of urbanization, indoor plumbing and home washing tools slowly developed, but manual washing remained the standard for a long time.
The introduction of mechanical washing machines in the early 20th century drastically changed laundering. Electric-powered agitators and drum washing machines removed the physical strain of manual scrubbing. Later, coin-operated laundromats appeared, especially in urban areas where small apartments did not have space for machines. These self-service laundry spaces were the first modern lavanderias, affordable and accessible to working families.
Today, lavanderias vary from small independent storefronts to ultra-modern automated facilities offering washing, drying, ironing, dry cleaning, stain treatment, pickup and delivery, mobile app scheduling, and eco-friendly washing systems. Some also serve commercial clients such as hotels, medical clinics, restaurants, uniforms, spas, and industrial workplaces. While customer needs and technology continue evolving, the central purpose remains the same: ensuring fabrics are clean, fresh, hygienic, and ready for use.
Types of Lavanderias
Lavanderias are not all the same, and their services differ based on audience, scale, and specialization. Below is a comprehensive overview of the most common categories:
| Type of Lavanderia | Description | Common Users |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Service Lavanderia | Clients operate machines themselves using coins, prepaid cards, or digital payment systems. | Students, tenants, travelers |
| Full-Service Lavanderia | Staff wash, dry, fold, iron, and package clothing for clients. | Busy professionals, families |
| Dry Cleaning Lavanderia | Uses chemical solvents instead of water for delicate fabrics. | Suits, evening wear, uniforms |
| Industrial Lavanderia | Handles high-volume laundry for industries. | Workers, factories, oilfields |
| Commercial Lavanderia | Serves businesses requiring regular textile cleaning. | Hotels, restaurants, hospitals |
| Eco-Friendly Lavanderia | Prioritizes energy efficiency, low water use, and green detergents. | Environment-conscious clients |
| On-Demand Lavanderia | Offers app-based pickup and delivery laundry. | Urban areas, online customers |
This diversity shows that lavanderias are not simply washing places; they have evolved into business models shaped by modern needs, urban mobility, improved hygiene requirements, and technology integration.
Common Processes Inside a Lavanderia
A professional lavanderia does not simply wash clothes; it follows scientific procedures to ensure fabrics are cleaned without damage, stains are properly treated, and hygiene standards are maintained. Understanding each step helps consumers appreciate the work that happens behind the scenes.
1. Fabric Sorting
Before washing, trained staff sort textiles based on:
- Color (dark, light, whites)
- Fabric material (cotton, silk, wool, synthetics)
- Washing instructions on care labels
- Level of soil (clean, stained, heavily soiled)
Correct sorting prevents color bleeding, fabric damage, shrinkage, and rough texture.
2. Stain Assessment and Pretreatment
Not all stains are the same. Oils, wine, grass, blood, ink, and rust require different stain removers and treatment durations. A professional lavanderia identifies stains and applies the correct pre-wash technique. This prevents unnecessary use of heat or chemicals, which could set the stain permanently.
3. Washing
This stage includes selecting:
- Water temperature
- Detergent type
- Machine agitation level
- Appropriate wash cycle time
For example:
| Fabric Type | Water Temperature | Agitation Level |
|---|---|---|
| Cotton | Hot or warm | Medium to high |
| Wool | Cold | Gentle |
| Synthetic blends | Warm | Low |
| Delicate fabrics | Cold | Very low |
Professional lavanderias often use industrial detergents that perform efficiently in lower amounts, saving resources while delivering superior cleaning.
4. Rinsing
Rinsing removes detergent residue, dirt particles, and chemical traces. Double rinsing may be necessary for baby clothes or medical linens to ensure complete removal of irritants.
5. Drying
Dryers must be selected and programmed based on fabric:
- Cotton tolerates high temperatures
- Synthetics require low heat
- Linen needs careful timing
- Wool should be air-dried
Incorrect drying temperature is one of the biggest causes of shrinking and fabric damage at home, but trained laundry staff prevent these mistakes.
6. Ironing and Finishing
Many lavanderias offer pressing, steaming, or hot-plate ironing to deliver crisp, wrinkle-free garments. Advanced facilities use steam tunnels for shirts and uniforms, offering a professional finish in shorter time.
7. Folding and Packaging
Clothes are folded or hung, sorted by client name, and neatly packaged. Some premium laundries fragrance packaging with mild hypoallergenic scents.
Essential Equipment Used in Modern Lavanderias
Modern lavanderias are sophisticated operations requiring reliable, heavy-duty machines capable of running continuously. Below is a breakdown of typical equipment:
| Equipment | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Industrial washing machines | High-capacity washers designed for frequent cycles |
| Commercial dryers | Fast-drying systems with programmable heat settings |
| Flatwork ironers | Used to iron linens, sheets, and large flat fabrics |
| Steam presses | Give crisp finish to shirts and uniforms |
| Fold-assist machines | Automatically fold large items efficiently |
| Water softeners | Improve washing results and machine longevity |
| Detergent dispensing systems | Precisely control chemical use |
| Barcode or RFID tracking tools | Track orders and reduce errors |
Choosing quality equipment ensures durability, speed, energy efficiency, and consistent customer satisfaction.
The Role of Staff and Training
People often underestimate how much knowledge laundry technicians must have. A professional lavanderia requires training in:
- Fabric composition and behavior
- Washing machine controls
- Chemical mixing and safety
- Stain science
- Customer service
- Order tracking
- Health and hygiene compliance
Inside a large lavanderia, staff positions may include:
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Counter receptionist | Accepts orders, handles customer queries, manages payments |
| Sorting and tagging staff | Organizes garments and attaches identifiers |
| Machine operators | Load washers and dryers, monitor cycles |
| Stain specialists | Perform manual stain removal |
| Finishers and pressers | Iron and package clothing |
| Quality controllers | Inspect garments before release |
This structured teamwork ensures that garments pass through the correct workflow without error.
Why People Choose Lavanderia Services
Lavanderias solve a wide range of personal and household challenges. Some of the strongest reasons include:
Time Savings
Laundry can consume hours of sorting, washing, dried, and ironing. Working individuals or families with busy schedules prefer outsourcing the task to free time for more productive or relaxing activities.
Small Living Spaces
Many city apartments lack washer and dryer hookups. College dorms also rely heavily on lavanderia access.
Professional Results
Experienced laundry staff understand fabrics scientifically, ensuring better stain removal, fresher feel, and higher longevity of textiles.
Cost Efficiency
Buying, maintaining, and repairing household machines can be expensive. In areas with high electricity or water costs, laundromat use may be cheaper.
Large or Bulky Items
Items like comforters, rugs, curtains, and athletic gear do not easily fit into small home machines. Professional facilities handle these effortlessly.
Lavanderias for Businesses and Institutions
Beyond household laundry, many industries rely heavily on reliable cleaning services:
| Industry | Items Cleaned |
|---|---|
| Hotels and resorts | Sheets, towels, staff uniforms |
| Hospitals and clinics | Bed linens, surgical gowns, scrubs |
| Restaurants and cafés | Table linens, kitchen cloths, uniforms |
| Manufacturing facilities | Workwear, safety garments |
| Gyms and spas | Towels, robes |
| Schools and colleges | Sports uniforms, hostel bedding |
Large operations require strict scheduling and inventory control. A commercial lavanderia must guarantee:
- Hygiene standards
- Consistent turnaround time
- Good stain removal
- Fabric longevity
- Volume handling capability
This makes commercial laundry not only a cleaning service but a crucial logistical partner.
Environmental Impact and Sustainable Lavanderias
Traditional laundry processes consume significant water, energy, and chemicals. However, modern lavanderias are shifting toward greener practices such as:
Low-Waste Detergents
Using concentrated, biodegradable formulas that dissolve easily and require less rinsing.
Water Recycling
Advanced machines reuse final rinse water for the next wash cycle, reducing consumption significantly.
Energy-Efficient Heating
Steam recycling and heat pumps lower electricity usage.
Ozone-Based Washing
Ozone systems disinfect in cold water, reducing energy and chemical usage, while delivering hospital-grade sanitation.
Machine Sensors
Automated sensors adjust:
- Water level
- Detergent dosage
- Wash cycle duration
This avoids waste and prolongs machine life.
Consumers increasingly prefer lavanderias that show environmental responsibility, and sustainability is one of the strongest competitive advantages in the modern laundry business.
Technological Innovations in Lavanderia Services
Technology is rapidly transforming the industry. Today’s advanced lavanderias may include:
Mobile Apps
Customers can schedule pickups, track washing progress, and make payments via smartphone.
Automated Service Lockers
Customers drop off laundry in secure lockers and retrieve it anytime after service completion.
RFID Tracking
Special tags ensure garments never get misplaced, improving accuracy for large-scale businesses.
Smart Machines
Commercial washers analyze load weight, soil level, and detergent type, then optimize cycles automatically.
Data Analytics
Laundry operators examine machine usage data to:
- Plan maintenance
- Reduce breakdowns
- Increase profitability
- Improve scheduling
All these innovations make operations smoother, faster, and more cost-effective.
How to Start a Lavanderia Business
Entrepreneurs often seek to open a lavanderia because demand remains constant regardless of economic cycles. However, successful setup requires planning, adequate capital, equipment selection, staffing, marketing, and location strategy.
Selecting the Location
A good lavanderia site should have:
- High residential density
- Foot traffic or street visibility
- Parking availability
- Low competition in the surrounding area
- Accessibility by public transport
Startup Investment Budget
Below is a simplified example of possible startup costs:
| Expense Category | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Lease and renovation | Medium |
| Industrial washers and dryers | High |
| Water treatment and plumbing | Medium to high |
| Business licenses | Low |
| Laundry supplies and chemicals | Medium |
| Staff hiring and training | Medium |
| Marketing and branding | Medium |
Exact numbers vary by country and city, but equipment and plumbing remain the largest initial investments.
Business Models
Entrepreneurs can choose from different systems:
| Model | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Self-service | Lower labor cost | Requires maintenance and supervision |
| Full-service | Higher income per customer | Increased staffing needs |
| Hybrid | Flexible for both markets | Complex management |
| Franchise | Brand recognition and support | Franchise fees |
| On-demand pickup & delivery | Wider reach | Requires a delivery fleet |
Customer Retention Strategies
Lavanderia customers stay loyal when they experience:
- Fast turnaround
- Transparent pricing
- No lost items
- Stain removal expertise
- Courteous service
- Clean environment
Loyalty cards, subscription plans, and mobile booking apps can further improve retention.
Customer Expectations in a Modern Lavanderia
Consumers increasingly demand professionalism beyond simply washing clothes. Key expectations now include:
- Clean and hygienic environment
- Friendly communication
- Digital payment options
- Consistent stain removal
- Clearly displayed pricing
- Reliable timelines
- Safe handling of delicate fabrics
- Fragrant, fresh but not overpowering scents
Meeting these expectations is crucial for building strong community reputation.
Challenges Faced by the Laundry Industry
Despite demand stability, lavanderias face several operational challenges:
1. Rising Utility Costs
Electricity, water, and gas bills heavily influence profitability. Efficient machines and recycling systems help manage this issue.
2. Chemical Disposal Regulations
Environmental compliance requires proper waste handling and sometimes expensive upgrades.
3. Machine Maintenance
Commercial equipment is durable but requires regular servicing. Unplanned breakdowns can halt operations and cause delays.
4. Staffing Challenges
Training new workers and retaining them in physically demanding roles is not always easy.
5. Competition
Low barrier to entry means many small laundries compete within the same neighborhood, making branding essential.
The Future of Lavanderias
The future of laundry services will be defined by:
Automation
Robotic garment sorting, folding machines, and smart workflows will reduce labor dependency.
Contactless Systems
Digital lockers, automated pick-up delivery tracking, and seamless billing will dominate urban markets.
Subscription-Based Laundry
Monthly packages offering wash-dry-fold services are gaining popularity in major cities.
Green Technology Integration
Biodegradable detergents, solar-powered equipment, and water-recycling systems will become industry standards.
AI-Driven Operations
Artificial intelligence may eventually predict:
- Busy hours
- Machine failures
- Fabric care adjustments
- Optimal detergent usage
Increased Industry Specialization
More lavanderias will focus on niche sectors such as:
- Wedding garment care
- Medical sterilized laundry
- Sports team uniforms
- High-end couture cleaning
Conclusion
A lavanderia is far more than a place to wash clothes. It represents a structured industry built on chemistry, mechanical engineering, customer service, and business management. From community washhouses to smart app-based automated facilities, lavanderias continue adapting to modern lifestyles, environmental priorities, and technological innovation. Their enduring importance lies in the universal human need for clean clothing—something that will never disappear. Whether run as a neighborhood self-service laundromat or a large commercial operation cleaning thousands of garments per day, the lavanderia industry remains an essential backbone of both domestic and industrial life.
FAQs
1. What does “lavanderia” mean?
Lavanderia is a term used in Spanish, Italian, and Portuguese languages referring to a laundry facility where clothes and textiles are washed, dried, and sometimes ironed.
2. Is a lavanderia only for self-service washing?
No. It can be self-service, full-service, commercial, industrial, or specialty based on the business model and the customers it serves.
3. What makes a modern lavanderia different from older laundromats?
Modern facilities use automated machines, eco-friendly detergents, app-based booking, RFID tracking, and faster, more hygienic washing systems.
4. Do lavanderias handle commercial clients?
Yes. Many serve hospitals, hotels, clinics, factories, restaurants, and gyms that require large-scale and regular textile cleaning.
5. Is opening a lavanderia profitable?
Yes, when managed efficiently. With good location, quality equipment, and customer service, lavanderias can generate stable income due to constant demand.