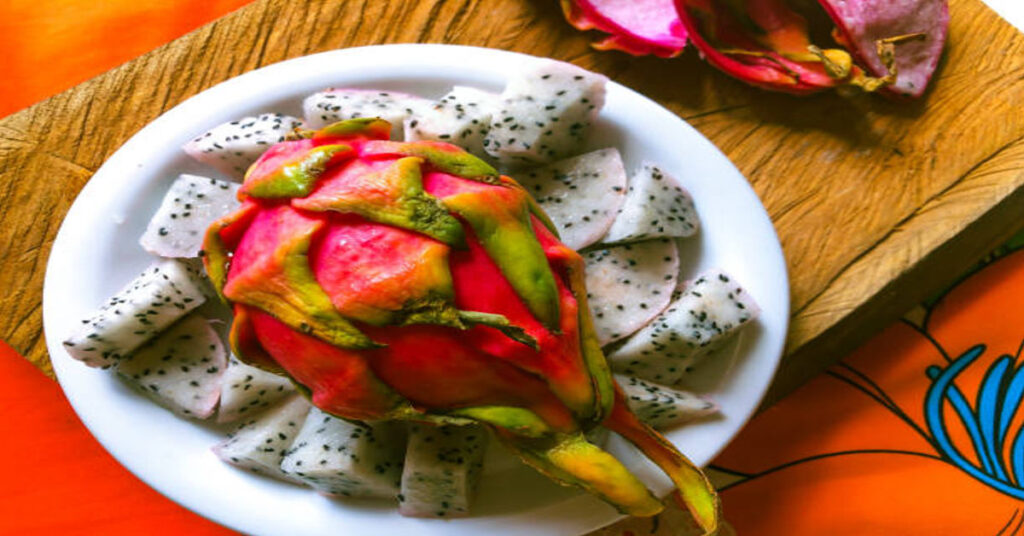
The fruit known as “Drachenfrucht” in German translates to “Dragon Fruit” in English. This name perfectly captures its stunning appearance—vibrant, fiery skin with green scales resembling a dragon’s hide and a soft, speckled interior that feels both exotic and magical. Beyond its striking looks, dragon fruit has become globally popular due to its refreshing taste, low-calorie profile, and impressive nutritional benefits.
In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore everything there is to know about Drachenfrucht—its English meaning, history, varieties, nutritional composition, cultivation process, health advantages, culinary uses, and more. Whether you are a fruit lover, a health-conscious eater, or someone simply curious about exotic foods, this guide will give you a deep understanding of why dragon fruit is considered a true treasure of nature.
1. What Is Drachenfrucht (Dragon Fruit)?
“Drachenfrucht” literally means dragon fruit in English. It is the fruit of a cactus species belonging to the genus Hylocereus and Selenicereus. Its scientific name, depending on the variety, is typically Hylocereus undatus (white-fleshed), Hylocereus costaricensis (red-fleshed), or Hylocereus megalanthus (yellow-skinned).
The fruit grows on climbing cacti that thrive in tropical and subtropical regions. Its unique outer appearance—with vivid pink or yellow skin covered in leafy scales—makes it stand out from most fruits. Inside, you’ll find soft, juicy flesh filled with tiny black seeds that are edible and rich in fiber.
The taste of dragon fruit is mild yet refreshing—often described as a mix between kiwi and pear, with subtle sweetness and a smooth texture.
2. Origin and History of Drachenfrucht
Dragon fruit originated in Central America, particularly in areas like Mexico, Costa Rica, and Nicaragua. Indigenous peoples cultivated it long before it spread to other regions. The fruit’s journey across the world began during the 19th century when French explorers introduced it to Vietnam and other parts of Southeast Asia.
Today, dragon fruit is cultivated in countries such as Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia, Israel, and the Philippines, as well as Australia, India, and parts of the United States (especially California and Florida).
Interestingly, in Vietnam, the plant is often referred to as “thanh long,” which also translates to “green dragon.” This connection further explains why the German term “Drachenfrucht” has such a mythical quality.
3. Varieties of Drachenfrucht (Dragon Fruit)
Dragon fruit comes in several varieties, each differing slightly in color, flavor, and texture. The most common types are white, red, and yellow dragon fruit.
Table 1: Main Varieties of Dragon Fruit
| Variety | Outer Skin Color | Flesh Color | Taste | Common Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hylocereus undatus | Pink or red | White | Mildly sweet | White Dragon Fruit |
| Hylocereus costaricensis | Deep pink or red | Red or magenta | Richer sweetness | Red Dragon Fruit |
| Hylocereus megalanthus | Yellow | White | Very sweet | Yellow Dragon Fruit |
1. White-Fleshed Dragon Fruit
This is the most common type seen in supermarkets. It has bright pink skin with white flesh speckled with black seeds. Its taste is mildly sweet and very refreshing, making it perfect for hydration.
2. Red-Fleshed Dragon Fruit
This variety has both red skin and red or magenta flesh. It’s slightly sweeter and juicier than the white variety, with a stronger flavor and higher antioxidant content.
3. Yellow Dragon Fruit
The rarest and often considered the sweetest, this variety has yellow skin with white flesh. The skin is spiky instead of leafy, and the taste is crisp, floral, and intensely sweet.
4. Nutritional Value of Drachenfrucht
One of the reasons dragon fruit has become so popular is its rich nutritional profile. It’s a low-calorie, high-fiber, antioxidant-rich fruit that provides a wide range of essential vitamins and minerals.
Table 2: Nutritional Value (Per 100g of Dragon Fruit)
| Nutrient | Quantity | Health Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 50–60 kcal | Low-calorie energy |
| Carbohydrates | 13 g | Natural sugars for energy |
| Fiber | 3 g | Improves digestion |
| Protein | 1.1 g | Aids tissue repair |
| Fat | 0.1 g | Very low fat |
| Vitamin C | 20 mg | Boosts immunity |
| Magnesium | 10 mg | Supports muscles and nerves |
| Iron | 0.6 mg | Promotes red blood cell production |
| Calcium | 18 mg | Strengthens bones |
| Antioxidants | High | Fights free radicals |
The balance of fiber and antioxidants makes dragon fruit especially appealing for those seeking a healthy, hydrating snack.
5. Health Benefits of Drachenfrucht
Dragon fruit is not only beautiful but also a powerhouse of health benefits. Let’s explore its numerous advantages in detail.
1. Strengthens Immunity
Thanks to its vitamin C and antioxidant content, dragon fruit helps strengthen the immune system, protecting the body from infections and diseases.
2. Improves Digestion
The tiny black seeds inside dragon fruit contain natural oils and fiber that support healthy digestion and bowel movement.
3. Regulates Blood Sugar Levels
The high fiber content helps regulate sugar absorption, making it a suitable fruit for people with diabetes when consumed moderately.
4. Supports Heart Health
Dragon fruit contains monounsaturated fats and antioxidants that reduce LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol) and improve cardiovascular health.
5. Aids in Weight Management
Being low in calories and rich in fiber, it keeps you full longer while promoting fat metabolism.
6. Enhances Skin Glow
Vitamin C and antioxidants reduce oxidative stress, helping to maintain youthful, radiant skin.
7. Promotes Better Sleep
Magnesium and natural sugars in the fruit help relax muscles and support better sleep quality.
6. How Dragon Fruit Grows – The Cultivation Process
Dragon fruit plants belong to the cactus family, making them uniquely suited to warm, dry climates. The plant is a climbing vine-like cactus that needs support to grow upright.
Table 3: Cultivation Requirements
| Growth Factor | Ideal Condition |
|---|---|
| Climate | Tropical/Subtropical |
| Temperature | 20°C–30°C |
| Soil | Well-drained sandy loam |
| Sunlight | Full to partial sunlight |
| Watering | Moderate (avoid overwatering) |
Stages of Growth
- Planting: Usually propagated from stem cuttings, which root easily.
- Flowering: The plant produces large white flowers that bloom at night—hence the name “Moonflower Cactus.”
- Pollination: Some varieties self-pollinate, while others require insects or human assistance.
- Fruit Development: Fruits mature within 30–50 days after flowering.
- Harvesting: Fruits are hand-picked when the skin turns bright and fully colored.
This growth cycle makes dragon fruit a fascinating agricultural crop—requiring patience but rewarding farmers with high yields.
7. Culinary Uses of Dragon Fruit
Dragon fruit’s mild flavor and beautiful color make it versatile in the kitchen. It can be used in sweet dishes, savory recipes, or simply eaten fresh.
1. Fresh Consumption
The simplest way to enjoy dragon fruit is to cut it in half and scoop out the flesh with a spoon.
2. Smoothies and Juices
Its juicy texture makes it a perfect base for smoothies and tropical juices. It pairs beautifully with mango, banana, or coconut water.
3. Salads
Combine dragon fruit with kiwi, orange, and pineapple to create colorful, nutritious fruit salads.
4. Desserts
Use dragon fruit in yogurts, puddings, ice creams, and even cakes for a tropical touch.
5. Savory Dishes
In modern cuisine, dragon fruit is used as a garnish for grilled seafood, or diced in spicy salads for a refreshing contrast.
Table 4: Common Culinary Uses
| Dish Type | Example | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Beverage | Dragon fruit smoothie | Hydrating and vitamin-rich |
| Salad | Fruit salad with mint | Refreshing and cooling |
| Dessert | Dragon fruit sorbet | Low-fat indulgence |
| Breakfast | Yogurt parfait | Energizing start |
| Savory | Dragon fruit salsa | Exotic flavor pairing |
8. Dragon Fruit in Global Culture
Dragon fruit holds symbolic significance in many cultures due to its exotic appearance and resilience.
- In Asia, it represents prosperity and luck. In Vietnam, dragon fruit is often used as an offering in temples.
- In Latin America, it symbolizes fertility and strength, as the cactus plant can survive in harsh climates.
- In Western countries, it’s associated with wellness, vitality, and healthy living—frequently featured in health magazines and cafés.
This cultural richness enhances its appeal as more than just a fruit—it’s a global symbol of nature’s creativity.
9. Storage and Handling Tips
To enjoy dragon fruit at its best, proper storage and handling are essential.
- Room Temperature: Uncut fruit can be kept for 3–5 days at room temperature.
- Refrigeration: Once cut, store it in an airtight container for up to 2–3 days.
- Avoid Freezing: While you can freeze it for smoothies, freezing may slightly alter its texture.
- Ripeness Check: A ripe dragon fruit will have evenly colored skin and a slight give when pressed.
Proper handling preserves flavor, texture, and nutritional quality.
10. Economic and Environmental Importance
Dragon fruit has significant economic value, especially in tropical regions where it supports local farmers. The plant is drought-tolerant, low-maintenance, and yields high profits per acre.
Additionally, it contributes to sustainable agriculture since it requires less water and fewer pesticides compared to other tropical crops. The cactus structure helps prevent soil erosion, making it an eco-friendly crop choice.
Table 5: Economic Advantages of Dragon Fruit Farming
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| High Yield | Up to 25–30 tons per hectare |
| Low Maintenance | Minimal pesticide use |
| Profitability | High due to demand in export markets |
| Sustainability | Drought-resistant and soil-friendly |
11. Fun Facts About Dragon Fruit
- Dragon fruit flowers bloom only at night and last for a single night.
- It’s nicknamed “moonlight cactus” or “queen of the night.”
- The seeds inside dragon fruit aid in natural detoxification.
- It can be used to make natural dyes due to its bright color pigments.
- Dragon fruit plants can live and bear fruit for over 20 years.
These facts show that Drachenfrucht isn’t just delicious—it’s a botanical wonder.
12. Dragon Fruit vs Other Tropical Fruits
Comparing dragon fruit to other tropical fruits highlights its uniqueness.
Table 6: Comparison with Other Tropical Fruits
| Fruit | Calories (per 100g) | Vitamin C (mg) | Fiber (g) | Taste Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dragon Fruit | 50–60 | 20 | 3 | Mildly sweet |
| Mango | 60 | 36 | 1.6 | Rich and sweet |
| Papaya | 43 | 60 | 1.7 | Soft and musky |
| Kiwi | 41 | 92 | 3 | Tangy and fresh |
| Pineapple | 50 | 47 | 1.4 | Sharp and tropical |
Dragon fruit offers a balance between taste and health—less sugary than mango or pineapple but richer in fiber than most fruits.
13. Potential Side Effects (Rare but Worth Knowing)
Although dragon fruit is safe for most people, a few may experience mild allergic reactions such as itching or swelling after consumption. These cases are rare and typically occur in individuals sensitive to certain fruit enzymes.
Overeating may also lead to temporary digestive discomfort due to high fiber intake. Therefore, moderation is always best—enjoy it as part of a balanced diet.
14. Future of Dragon Fruit in Global Markets
The popularity of Drachenfrucht continues to rise as consumers seek nutritious, visually appealing superfoods. The fruit’s potential in the health and cosmetic industries is expanding—its extract is used in skincare products, beverages, and supplements.
Given its sustainability and nutritional profile, dragon fruit is poised to become a staple in global healthy-living trends for decades to come.
15. Conclusion
“Drachenfrucht” in English is “Dragon Fruit,” a fitting name for one of nature’s most extraordinary creations. With its vibrant color, refreshing taste, and outstanding nutritional value, it bridges the gap between beauty and health.
From the deserts of Central America to the farms of Southeast Asia, this cactus fruit has conquered hearts and plates across the world. It nourishes the body, beautifies the skin, and contributes to sustainable agriculture.
Whether you enjoy it fresh, blended, or added to your favorite dishes, dragon fruit remains a perfect example of how simplicity and nature’s brilliance come together. Every bite is a taste of tropical vitality, a reminder of our planet’s diversity, and a symbol of health and abundance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the English name of Drachenfrucht?
The English name of Drachenfrucht is Dragon Fruit, also known as pitaya or pitahaya in some regions.
2. Where does dragon fruit originally come from?
Dragon fruit originated in Central America, but it is now widely cultivated in Asia, especially in Vietnam and Thailand.
3. What are the health benefits of dragon fruit?
It boosts immunity, aids digestion, regulates blood sugar, promotes healthy skin, and supports heart health due to its antioxidants.
4. How do you know if a dragon fruit is ripe?
A ripe dragon fruit will have evenly colored skin and feel slightly soft when gently pressed, similar to a ripe kiwi.
5. Can dragon fruit help in weight loss?
Yes. It’s low in calories, high in fiber, and helps control appetite, making it ideal for healthy weight management.